 If you have been undergoing conservative treatment for your neck, back or joint pain, muscle spasm, shortened muscles or fibrous adhesions for more than eight weeks with little to no improvement, you may be a candidate for manipulation under anesthesia or MUA.
If you have been undergoing conservative treatment for your neck, back or joint pain, muscle spasm, shortened muscles or fibrous adhesions for more than eight weeks with little to no improvement, you may be a candidate for manipulation under anesthesia or MUA.
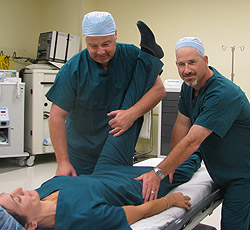
MUA involves the use of spinal manipulations, stretches, and postural or articular kinesthetic manuevers to break up adhesions and scar tissue in and around the spine. In this procedure, the patient may be subjected to general anesthesia, mild sedation or localized anesthesia. Because of the use of sedatives or anesthesia, the procedure is conducted by a team of anesthesiologists, doctors and chiropractors at either a hospital or surgery center.
This treatment option is recommended for patients who are suffering from neck, back and spinal conditions and do not respond to other types of treatments like physical therapy or chiropractic. Before undergoing MUA, a candidate will have to undergo a series of tests including imaging tests like X-rays and CT scans, blood tests, EKG, nerve conduction velocity and musculoskeletal sonograms.
There may be instances wherein a candidate is deemed not to be a good candidate for MUA. These include patients who have circulatory or cardiovascular disorders, acute gout, bone tuberculosis or weakness, spinal osteoporosis and other bone and spinal issues.
What should you expect if you are considered a good candidate for this procedure?
In this procedure, the patient is usually treated for three consecutive days using manipulative techniques and stretches which are not possible because of the pain and resistance usually associated with these methods without the aid of anesthetics. The use of anesthesia offers several advantages. First, muscle spasm is prevented, allowing spinal movement. Sedatives can also inhibit the nerves which may be irritated without the use of anesthetics. Finally, anesthetics allow complete muscle relaxation, allowing the specialist to stretch the affected muscles and break down adhesions.Typically, MUA is complemented by the use of strengthening and stabilization regimens a few weeks after the procedure to facilitate recovery and prevent the recurrence of the problem.
How effective is MUA?
Numerous studies attest to the efficacy of MUA in treating various conditions. In one of these studies, among patients who have been suffering from back pain for more than 10 years, 87 percent reported recovery. In another study, 71 percent out of 723 subjects reported a marked improvement in their conditions while more than 25 percent reported that they were able to attain some semblance of normalcy.















